
Intelligence databases and role of technical interoperability of Open Data
Image source: Dall. e
Recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs), alongside growing competition in the data sector, have significantly heightened the demand for enhanced open data interoperability. Companies are now fiercely competing on the basis of data, technology, and processing power. The scale of data used to train these models has expanded dramatically, shifting from millions to billions of tokens. This escalation highlights the critical need for scalable and efficient data integration to keep pace with the rapid evolution of LLMs. As interoperability requirements evolve, the necessity for massive data integration from various sources has become increasingly important. Open data interoperability plays a pivotal role in the development of data-oriented models, particularly through technical interoperability, which paves the way for the creation of new data products and the advancement of decision systems integrated with databases.
For example, modern databases are now being developed where data and AI models coexist and evolve together with the influx of new data. These databases integrate diverse data sources—structured, unstructured, and semi-structured—alongside AI engines, which may include machine learning, deep learning, and even modern LLMs. MindsDB is one such example of a modern database that exemplifies this integration. Technical interoperability of open data is crucial for these modern databases. Consider an open data portal as a source of data, which could be stored in various types of databases (e.g., vector, SQL, NoSQL). The open data portal requires a bridge API to feed data into the intelligent database. Once the data is ingested, a model can be selected based on the specific scenario. For instance, if the data is time-dependent, a time-series model available in the intelligent database can be chosen, or a custom-trained model can be applied. In this way, technical interoperability, supported by API solutions, facilitates seamless integration and model application. This concept is illustrated in the flow diagram in Figure 1.
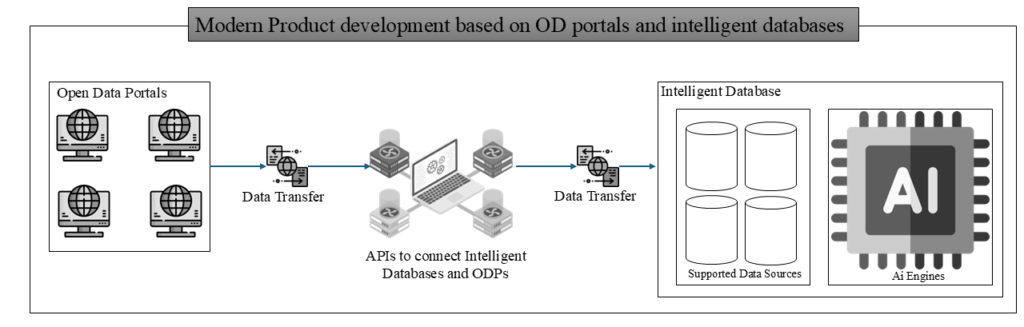
The scenario illustrates a cutting-edge approach to product development utilizing intelligent databases, with an Open Data portal serving as a crucial data source for model development. Whether using tailor-made or pre-trained models, the intelligent database allows for seamless integration and processing of data, ultimately producing ready-to-use models or products that support informed decision-making. These models can also be shared with other entities for reuse or further training, significantly enhancing the convenience and utility of data and applications for open data users. This approach not only accelerates the development process but also fosters greater collaboration and innovation across the data ecosystem. In conclusion, enhancing the technical interoperability of open data—particularly in terms of data transfer and access protocols—can significantly boost its utility in accelerating product development in today’s fast-paced, data-driven era. Improved interoperability ensures that data can be more easily integrated, accessed, and utilized, paving the way for more efficient innovation and the creation of advanced, ready-to-use products.
Use-case: Open Technologies Alliance (GFOSS – https://gfoss.eu/) is working on an API called GLOSSAPI to address this technical interoperability gap. The API is designed to extract Greek text from open sources and convert it into a format suitable for intelligent databases, enabling the categorization of the Greek language into various sub-classes. This dataset will be instrumental in the development of a large language model (LLM). I am actively contributing to the development of this API (https://github.com/eellak/glossAPI). My contributions to the GLOSSAPI project are visible in the GitHub repository of the project as shown in Figure 2.
Author:
Mohsan Ali
PhD Scholar
Lab: Information Systems Laboratory (ISL),
Dept.: Department of Information and Communication Systems Engineering (ICSD),
Uni.: University of the Aegean, Samos, Greece
Email: mohsan@aegean.gr | Tel + 30 698 6683 130
Project(s): Towards a sustainable Open Data ECOsystem (ODECO)
Profile Links: ISL | ICSD | Github | ODECO | ResearchGate | Google Scholar | Twitter | LinkedIn


