In this technological era, Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the globe and AI is about to change the world, but the problem is no one is quite sure how. AI stands at the forefront of technological innovation, poised to reshape industries and alter our daily lives profoundly. Some people look at the quick development over the last year and think there are chances to free creativity, automate everyday tasks, and find new ways to learn. Some people worry that this technology may cause more negative changes to our life, such as spreading fake information, reducing employment opportunities, and even endangering our physical safety if we don’t regulate it.

Who’s using AI?
Nowadays, AI is suddenly everywhere. For those of us with a background in computer science, most of the computer scientists know somehow how to use AI (what kind of AI model) for what kind of data. The rapid advancements in AI, from traditional machine learning to generative AI and large language models (LLMs) drive AI not just in the tech world but also in society and offer a mixture of excitement and concern. Concerns about cheating in schools with ChatGPT, being fooled by AI-generated pictures, and artists being ripped off or even outright replaced. However, regarding these specialized AI solutions, there has been very little adoption of these new tools despite extensive media attention. Additionally, younger users have a far higher amount of familiarity with these technologies. Also, people are eagerly anticipating the world-changing effects of AI, even though these technologies have seen very little use so far. We will see in our next section about how AI is being used, but before going onto let’s understand a bit more about how LLMs work. Basically, Large Language Models (LLMs) generate text that resembles human language by utilizing deep learning techniques to identify patterns in enormous quantities of textual data. These AI models are susceptible to biases, disinformation, and time constraints due to their limited knowledge and precision, which are dependent on the data they were trained on. In order to preserve their impartiality and dependability, it is imperative that they provide consistent updates and conduct a thorough examination of ethical implications.
How is AI being used?
The use of AI has already become common in our everyday lives. Time management, smart home device control, and entertainment are just a few of the many uses for virtual assistants like Google Assistant, Siri, and Alexa. These systems are designed to be more user-friendly and intuitive by using advanced natural language processing (NLP) methods. Our entertainment experiences are enhanced by AI-driven recommendation engines on platforms like Spotify and Netflix. These engines utilize deep learning methods and collaborative filtering to offer material that is suited to our interests.
The current rise in the usage of AI has been driven mostly by generative AI, which includes systems that can produce text, assist with idea generation, edit written work, and even create visuals, sounds, and videos. The following figure shows the search, create stories, brainstorming with AI, writing emails, data analysis and art dominate current AI use.
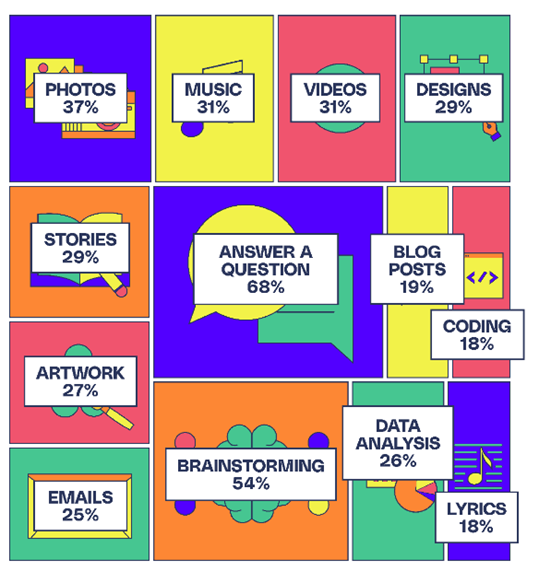
People compose songs, write novels, and edit images. Most importantly, individuals have begun asking AI systems questions, which has led some to speculate that chatbots such as ChatGPT, perplexity, and Gemini etc. might eventually replace search engines.
The Hope: Towards a brighter future with AI
AI’s transformative potential in healthcare is perhaps its most compelling promise. AI-driven diagnostic tools have made remarkable strides, surpassing human capabilities in speed and accuracy for conditions like cancer. These tools analyze medical images and patient data, identifying patterns that might elude even the most experienced clinicians. Moreover, AI facilitates the development of personalized medicine, tailoring treatments to an individual’s genetic profile and medical history, thereby improving efficacy and outcomes.
The availability of AI technologies has greatly increased the possibility for humans to achieve previously unimaginable levels of productivity. These technologies make it feasible for “ordinary” individuals to do things that were previously thought to be impossible, thanks to their advanced algorithms and machine learning capabilities. Individuals may now do what used to want large teams or specialist knowledge by using the almost limitless potential of AI. The following figure shows how AI is expanding and what people can create using AI.
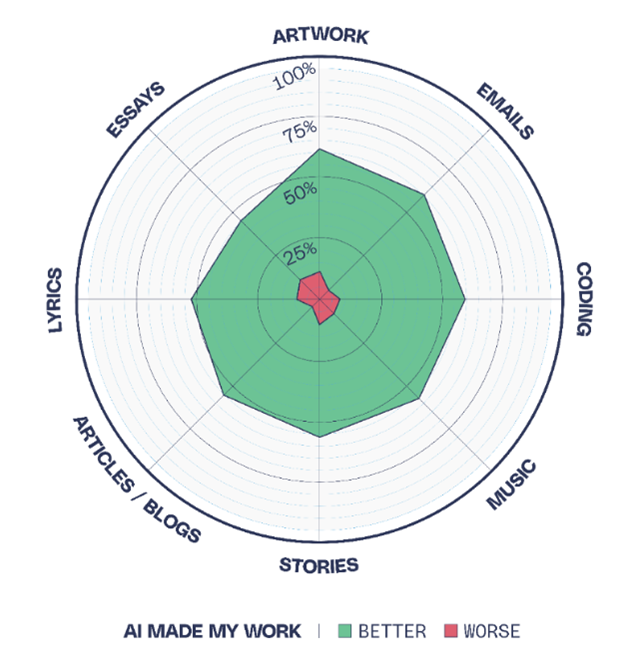
The role of AI in advancing scientific research cannot be overstated. AI systems are adept at processing and analyzing vast datasets, uncovering insights that can drive innovation. In climate science, for instance, AI models predict weather patterns and simulate climate change scenarios, providing critical data for policymakers. In biology, AI accelerates drug discovery by predicting molecular interactions and identifying potential drug candidates faster than traditional methods.
The Fear: The concerns around AI
Although AI has great potential, it also gives rise to significant concerns, notably with regards to the replacement of jobs. With the increasing capabilities of AI systems, there is a rising concern that they may make several occupations redundant, particularly in industries such as manufacturing, transportation, and customer service. Moreover, AI image generators such as Midjourney and Stable Diffusion provide a good illustration to examine wider concerns related to generative AI. These algorithms are taught using vast quantities of data obtained by scraping the web, often without the knowledge of the original creators. Although there is intense controversy around the ethics, the legality of this technique is presently under scrutiny in many cases. These ideas are rapidly expanding to other generative arts, such as AI music production.
The desire to exert control over AI technologies is not limited to tech elites. “Regulations and laws need to be developed regarding the development of AI,” is exactly what we were thinking about. The EU AI Act is now being implemented, while in the US, there are ongoing hearings to establish a legislative framework specifically for regulating AI. There is a widespread need for more openness and accountability in AI systems. For example, a significant majority of people endorse the concept of detecting deepfakes generated by artificial intelligence.
Resources:
- https://www.aratek.co/news/how-artificial-intelligence-ai-is-used-in-biometrics
- https://www.chcf.org/blog/ai-future-health-care/
- https://www.forbes.com/sites/cognitiveworld/2019/10/31/should-we-be-afraid-of-ai/
- https://www.kickframe.com/newsletter/2023/8/8/digital-trends-070123
- https://www.digitalfirstmagazine.com/10x-people
Authors:
Abdul Aziz, University of Zaragoza

Umair Ahmed, University of Camerino



